Six Sigma / 6σ – Smart Factory Glossary
Six Sigma, also known as 6σ, is a standardized and data-driven methodology to improve processes based on statistical values. Its aim is to optimize processes until they are virtually flawless. Companies use Six Sigma to reduce errors and defects and increase quality. The methodology analyzes the current status, identifies weak points in a process, and eliminates them.
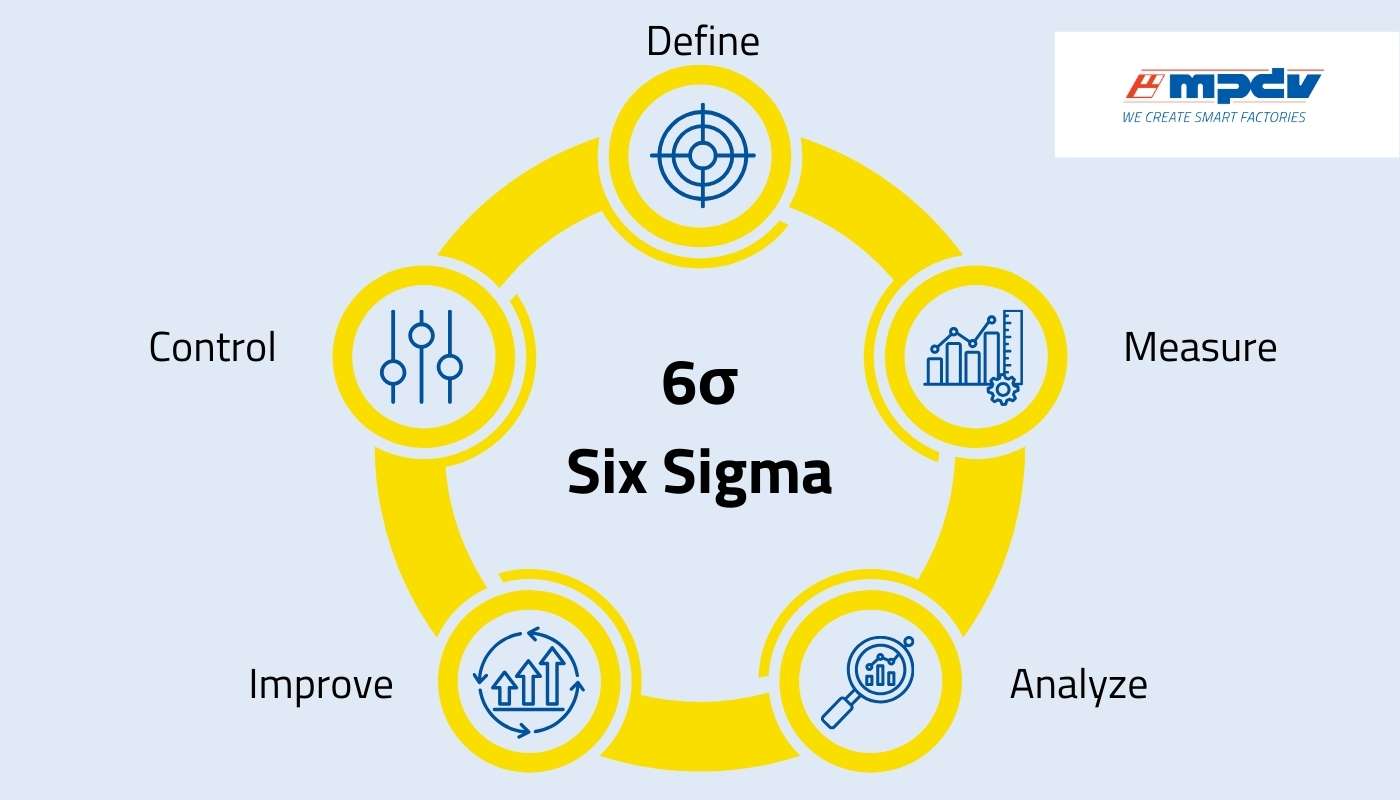
Six Sigma aims to achieve near-perfect quality, which means that errors or defects are not accepted. The DMAIC methodology is made up of five phases:
- Define: Clearly specify problem, objectives, and customer requirements.
- Measure: Collect data and analyze the as-is status.
- Analyze: Identify causes for defects and variations.
- Improve: Develop solutions and optimize processes.
- Control: Monitor improvements and sustain gains.
The name Six Sigma is derived from the Greek letter σ used in statistics as the symbol for the standard deviation according to the Gaussian law of normal distribution.
Source
- Schleupner, Linus/MES D.A.CH Verband e. V.: Fachlexikon MES & Industrie 4.0, 5. Aufl., Berlin Offenbach, Deutschland: VDE Verlag GmbH, 2022, S. 108-109.
Would you like more information? We are happy to help.
Just fill in the form below. We will take care of your inquiry promptly.